The symptoms of zinc deficiency vary widely among individuals. Zinc insufficiency manifest with multifarious indications based on the level of shortfall, food habits, gender of the patient, age group, general health status and presence of other diseases.
Growth retardation and weight loss
If the insufficiency is during pregnancy, the newborn shows birth defects and low birth weight. There is retarded physical and mental growth in affected children. Stunted growth, bowed limbs, dwarfism, scoliosis, pectus excavatum and poor reproductive growth are observed in children.
Impairment of cognitive and motor function
In adults, cognitive impairment, memory impairment, attention deficits, sleep problems and generalized disorganization of behavior are observed. In children learning of motor skills and memory functions are affected.
Decreased appetite
Anorexia or decreased appetite is among the initial indication of insufficiency. As anorexia and decreased food intake are causes of deficiency, a vicious cycle gets created.
Decreased sense of taste and smell
Zinc is necessary for the growth, development and function of taste and smell sensors and receptors.
The impairment of smell and taste senses is found to reverse with supplementation.
Diarrhea
Frequent diarrhea and stomach infections are symptoms of zinc deficit.
In the third world, zinc and ORS are of top priority in child patients suffering diarrhea, as invariably they show deficit of this trace mineral.
Degenerative diseases
Rapid progress in age related macular degeneration (AMD) and age-related eye disease (ARED) and loss of visual acuity are encountered.
Night blindness, myopia and photophobia may be due to zinc deficit.
Impaired reproductive system
Zinc insufficiency symptoms in women include defective, late and retarded growth of primary and secondary reproductive developments. Smaller breasts, narrow hips, disturbance of menstrual periods, fertility problems, pre-eclampsia in pregnancy and pre-menstrual syndrome are some of the effects.
Zinc deficiency indications in men include hypogonadism, defects in testes, defective primary and secondary reproductive development, fertility problems, loss of libido, impotence and aspermia.
Depression in immune functions
Production of antibodies declines and there is impaired function of T-lymphocytes, neutrophils and macrophages. There is marked increase in infections especially of the respiratory system.
Frequent attacks of flue and cold are observed. There is increased susceptibility to infections like pneumonia and there is increased allergic sensitivity.
Skin ailments
Frequent incidences of skin ulcers, acne, dermatitis, dry skin rash, psoriasis and eczema are symptoms of zinc deficiency.
Wounds get easily infected and take longer time to heal.
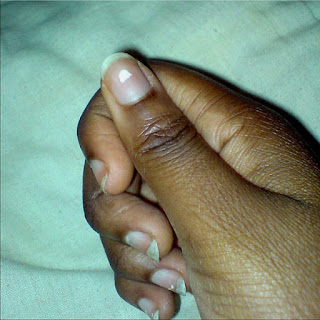
White spots and transverse lines on nails are zinc deficiency symptoms. Hangnails, inflammation of nail cuticles, nail infections, brittle nails, thin nails and poor nail growth are also observed. Hair loss (Alopecia) and dandruff are found to resolve with supplementation.
Enlargement of the prostate gland
Prostate gland has high concentration of zinc and benign enlargement of prostate gland and the resultant increased frequency of urination or inability to urinate are telltale warnings of shortage of the mineral.
Auto-immune diseases
The presence of auto-immune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis may be indications for underlying persistent shortage.
Psychological disorders
Psychological disorders and emotional disturbances like frequent mood changes, depression, sudden fright, low self-esteem, eating disorders, schizophrenia and emotional instability are some symptoms encountered in individuals with deficit in intake of this trace mineral.
Current topic : Symptoms of zinc deficiency


No comments:
Post a Comment